understanding differential thermostats: a natural approach to temperature control
Release time:2025-03-05 21:36:47
A differential thermostat is a type of temperature control system that is widely used to regulate the temperature of a system by comparing two different temperature readings. It plays a crucial role in various applications, particularly in energy conservation systems, heating, and cooling processes. What sets a differential thermostat apart is its natural approach to maintaining a stable temperature, especially by utilizing the differences in temperature between two distinct points.
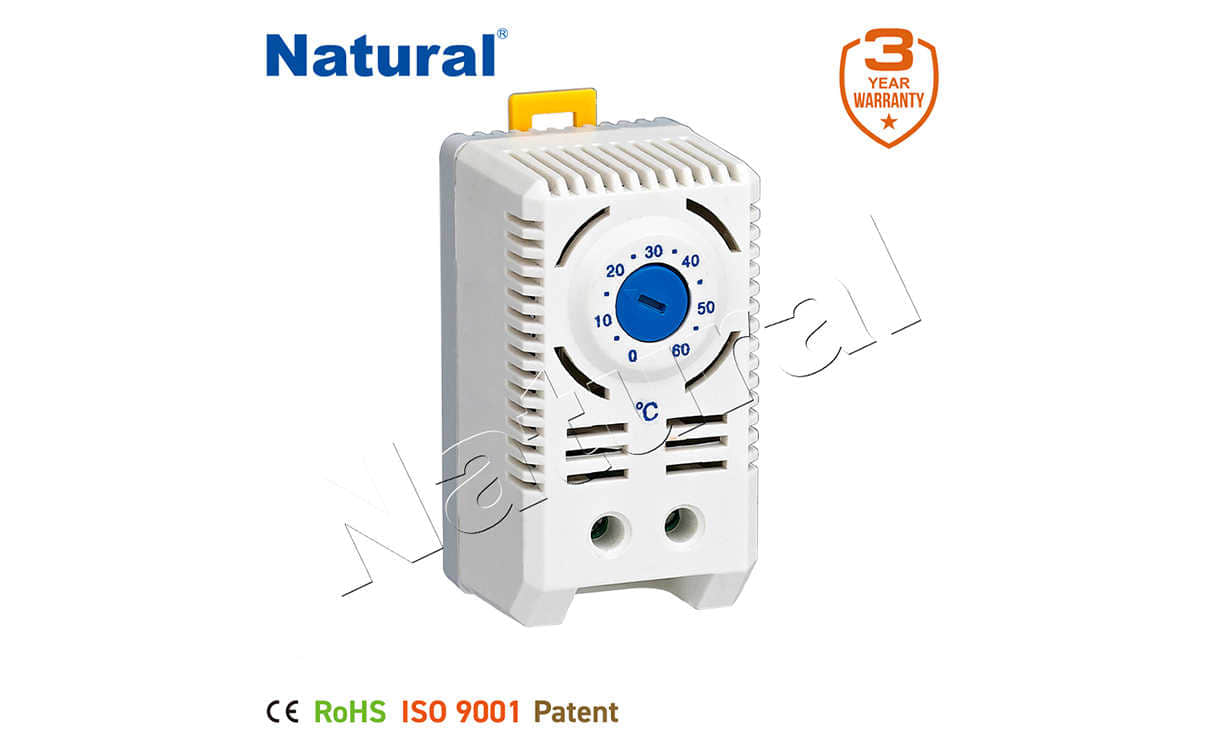

The Basics of Differential Thermostats
A differential thermostat works by monitoring the temperature difference between two locations. In essence, it acts as a comparison tool: if the temperature at one sensor rises above the temperature at the other, the thermostat activates or deactivates a device (like a heating or cooling unit) to restore the balance. This kind of system is often seen in solar water heating systems, where it compares the temperature of the water in the collector panels to the temperature of the water in the storage tank. If the collector is hotter than the tank, the thermostat will allow the heat to transfer from the collector to the tank.


 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent