the role of semiconductor heaters in modern technology: a natural approach
Release time:2025-04-23 07:53:21
Semiconductor heaters are becoming increasingly integral to various modern applications, from energy-efficient home heating systems to sophisticated industrial machinery. Their importance lies not only in their ability to provide precise temperature control but also in their energy efficiency and potential to work seamlessly with renewable energy systems. In this article, we’ll explore what semiconductor heaters are, how they function, and why they represent a natural evolution in thermal management technology.
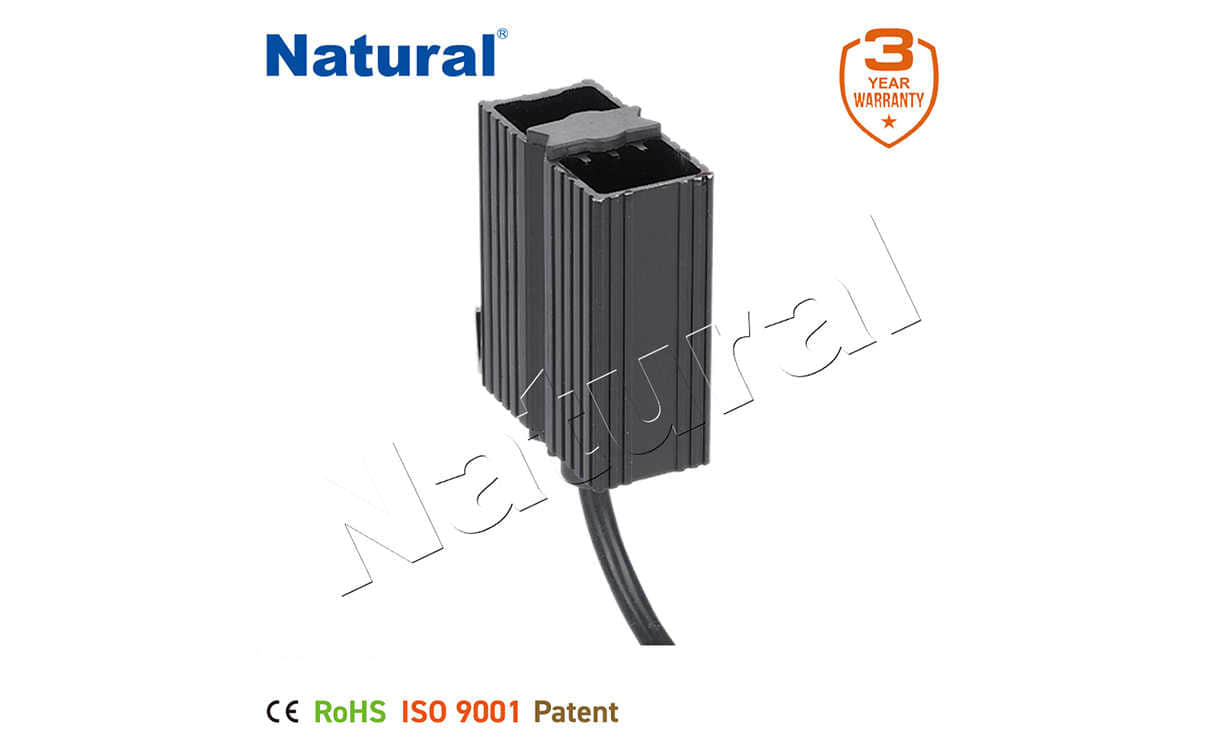

What Are Semiconductor Heaters?
Semiconductor heaters are electronic devices that utilize semiconductor materials—typically silicon or other advanced compounds—to generate heat. Unlike traditional resistive heaters that rely on metal filaments or coils, semiconductor heaters exploit the unique properties of semiconductors, such as their ability to control electrical current flow with precision. When an electric current passes through a semiconductor material, it encounters resistance, which results in the generation of heat. The amount of heat produced can be finely tuned by adjusting the amount of current or the type of semiconductor material used.
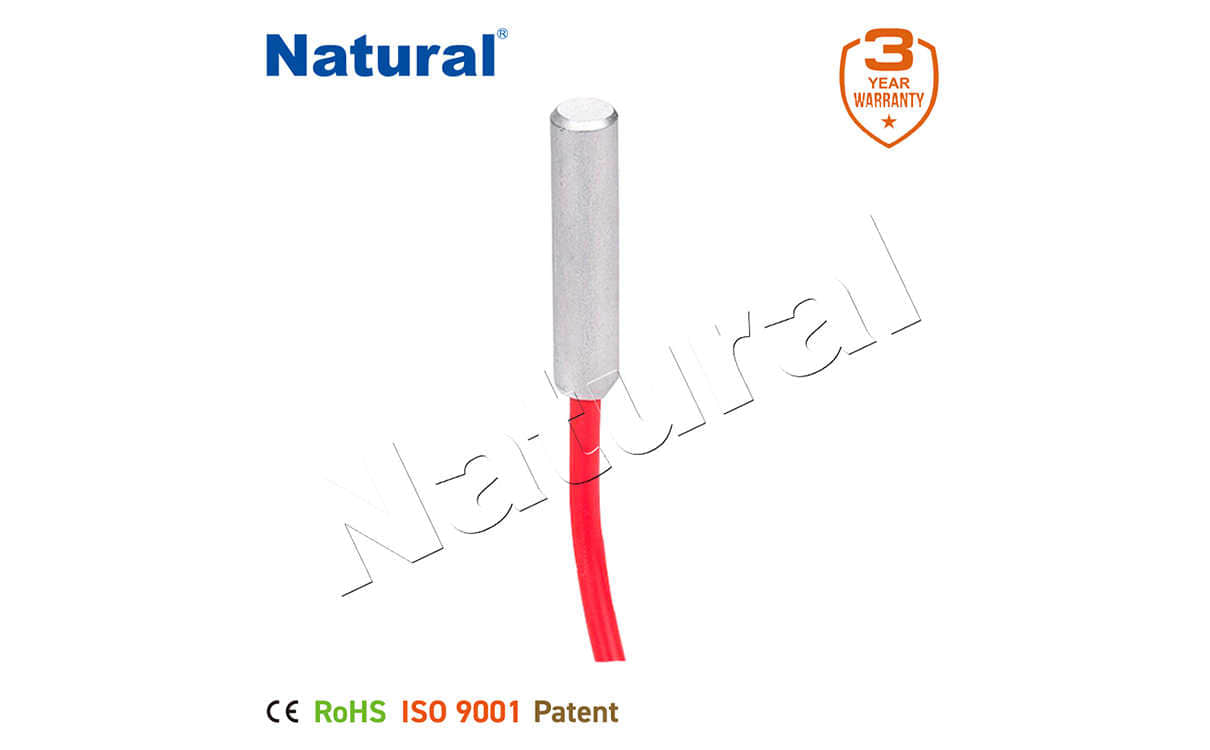


 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent
 28 items Patent
28 items Patent